Artificial Intelligence- Introduction
From Science Fiction to Reality: Understanding the AI Revolution
“Artificial Intelligence” once lived purely in the realm of fantasy. Today, it’s become one of technology’s most transformative forces, with virtually every tech company working on AI applications—whether they realize it or not.
My own AI journey began in movie theatres. Like many others, I first encountered the concept through sci-fi films, particularly Terminator and Iron Man. These movies presented AI’s dual nature perfectly: Terminator’s Skynet showed us the potential nightmare scenario—AI as humanity’s greatest threat—while Iron Man’s JARVIS demonstrated the dream—AI as our most capable ally. This contrast between destructive and constructive AI applications has shaped public perception ever since.
Curiosity sparked by countless news headlines and heated debates led me to dive deeper into this field. What I discovered was far more nuanced and fascinating than any Hollywood portrayal.
Defining Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence encompasses the broad field of creating systems that mimic human intelligence. Think about what human intelligence actually involves: logical thinking, reasoning, complex calculations, problem-solving, continuous learning, and perception of the world around us.
AI mirrors these capabilities in compelling ways. While humans rely on creativity to generate novel solutions, AI trained on massive datasets shouldn’t be underestimated. Humans might produce one brilliant, out-of-the-box idea, but AI can generate countless variations based on patterns in its training data—and even customize solutions for specific needs and contexts.
This isn’t about replacing human creativity; it’s about augmenting our capabilities in ways we’re only beginning to understand.
The Deeper History Than You’d Expect
AI research stretches back much further than most people realize. I initially assumed AI development began alongside the internet boom, but the reality surprised me—this field has been evolving for over seven decades.
Key Milestones in AI Development
1950: Alan Turing introduces the Turing Test (a method to assess whether a machine can exhibit human-like intelligence by having a judge converse with both a human and machine—if the judge can’t tell them apart, the machine passes).
1956: The Dartmouth Conference formally establishes AI as a research field. Led by John McCarthy and Marvin Minsky, this gathering coined the term “Artificial Intelligence” and set the academic foundation for everything that followed.
1997: IBM’s Deep Blue defeats world chess champion Garry Kasparov, proving machines could outthink humans in complex strategic games.
2011: IBM Watson wins Jeopardy! (an American television quiz show requiring broad knowledge and wordplay), demonstrating sophisticated natural language processing.
2014–2016: Virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa enter mainstream adoption, making AI interaction part of daily life.
2023–2025: Breakthrough advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) and autonomous systems reshape entire industries.
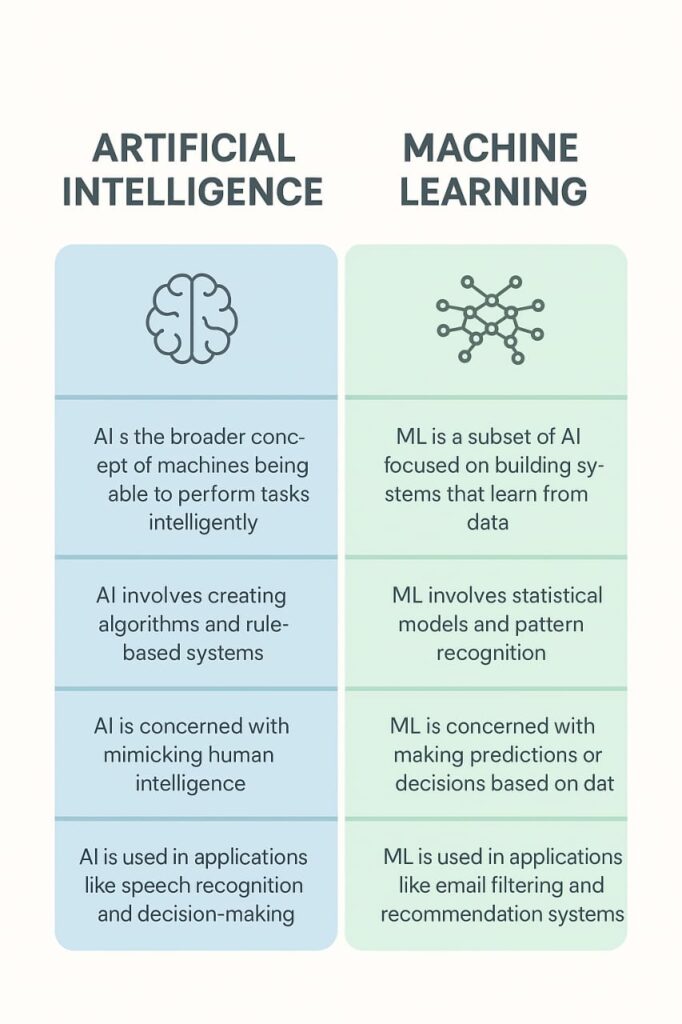
AI vs. Machine Learning: Clearing Up the Confusion
Initially, I thought AI was simply an advanced version of Machine Learning. We’re all familiar with ML applications—image recognition systems, search engines, spam filters, and e-commerce recommendation engines. But this perspective was backwards.
Machine Learning is actually a subset of Artificial Intelligence. In ML, models learn patterns from data and improve automatically without explicit programming for each task. The more data they process, the more efficient they become. Google’s search engine exemplifies this perfectly—constantly learning and refining results based on user behavior.
Think of ML as the “learning” form of AI, though typically limited to specific tasks. It’s like a specialist who becomes increasingly expert through focused training.
Understanding the Distinction
The Visionaries Who Built AI
Pioneering Minds
- John McCarthy: Coined “Artificial Intelligence” and pioneered AI programming languages
- Alan Turing: Proposed foundational concepts including the famous Turing Test
- Geoffrey Hinton: Pioneer of deep learning and neural networks (often called the “Godfather of AI”)
- Andrew Ng: Influential educator and entrepreneur, co-founder of Google Brain and Coursera
- Fei-Fei Li: Leading researcher in computer vision and AI ethics
Organizations Driving Innovation
- Google DeepMind: Pushing frontiers in reinforcement learning and AI research
- OpenAI: Developer of advanced Large Language Models and tools like ChatGPT
- IBM Research: Historic contributor with ground-breaking systems like Watson
- Microsoft AI Research: Driving enterprise AI innovations and integration
- Stanford HAI: Focusing on ethical and human-centred AI development
- Baidu AI Labs: Major player in AI research, especially across Asia
Why AI Exploded Now
If researchers have worked on AI for decades, why did the boom happen so suddenly—especially after 2020? Several factors converged perfectly:
Unprecedented Computing Power: Affordable GPUs and cloud infrastructure finally made training massive AI models economically viable. (NVIDIA’s dramatic market surge tells this story perfectly—their chips became the pickaxes of the AI gold rush.)
Breakthrough Algorithms: Deep learning and transformer models didn’t just improve AI capabilities—they supercharged them, making previously impossible tasks achievable.
Market Demand Alignment: Businesses desperately needed automation, personalization, and deeper data insights. AI provided solutions to real problems at exactly the right moment.
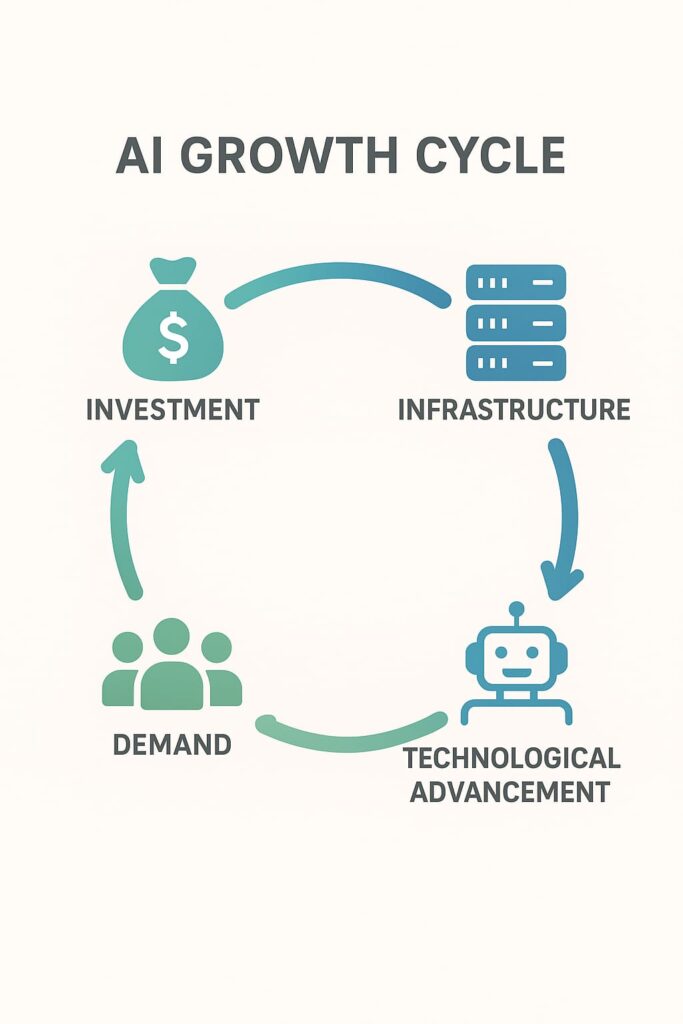
Post-Pandemic Priorities: The global crisis made efficiency and cost reduction business imperatives. AI fit these needs perfectly, creating massive investment momentum.
This created a powerful feedback loop: investment enabled infrastructure development, which accelerated technological advancement, which increased adoption and demand, which attracted more investment.
Real-World AI Applications
Healthcare Transformation
AI enables early and accurate disease diagnosis, including tumor detection that often surpasses human radiologists. These systems accelerate drug discovery processes and enable personalized treatments tailored to individual patient profiles.
Financial Revolution
From sophisticated fraud detection to algorithmic trading and comprehensive risk assessment, AI is reshaping how financial institutions operate and make decisions.
Transportation Evolution
Autonomous vehicles represent just the beginning—AI optimizes logistics networks, manages traffic flow, and reimagines how people and goods move through the world.
Retail Reinvention
Personalized recommendations, intelligent customer service chatbots, and supply chain optimization demonstrate AI’s versatility across consumer-facing industries.
The Dark Side We Can’t Ignore
However, AI’s misuse creates genuine risks:
- Sophisticated Fraud: Criminals leverage AI for identity theft, deepfake creation, and advanced phishing schemes
- Misguided Implementation: Some corporations replace human workers with machines instead of using AI to enhance productivity and create new opportunities
- Large-Scale Displacement: Fields like customer service face significant job losses without adequate transition planning
Navigating AI’s Challenges
Ethical Deployment
AI remains fundamentally a tool—it can elevate society or cause tremendous harm depending on how we develop and deploy it. The responsibility lies with creators and users.
Addressing Bias
Training data must be carefully curated and constantly evaluated to prevent harmful algorithmic biases that can perpetuate or amplify existing societal inequalities.
Managing Workforce Transitions
While history suggests new job categories will emerge, current layoffs and reduced hiring create immediate hardship that demands thoughtful policy responses.
Building Public Trust
Widespread scepticism about AI—particularly in critical areas like governance and healthcare—represents a significant barrier to beneficial adoption.
Embracing an Unstoppable Future
Innovation cannot be stopped, but it can be guided. Throughout history, major technological advances faced resistance and legitimate concerns. Some jobs disappeared (think coachmen and typewriter operators), while entirely new industries emerged (automotive engineering and digital content creation).
AI represents both disruption and unprecedented opportunity. Rather than resist this transformation, our best strategy is to learn, adapt, and shape AI development responsibly.
The future isn’t something that happens to us—it’s something we create together. Let’s make sure we build an AI-enhanced world that serves humanity’s best interests.
Turing, A. (1950). Computing Machinery and Intelligence. Mind, 59(236), 433–460.
→ For the Turing Test.
McCarthy, J., Minsky, M., Rochester, N., & Shannon, C. (1955). A Proposal for the Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence.
→ For the Dartmouth Conference 1956.
IBM. (2011). IBM Watson Wins Jeopardy! IBM Newsroom.
→ For IBM Watson’s victory in Jeopardy!
Campbell, M., Hoane Jr, A. J., & Hsu, F. H. (2002). Deep Blue. Artificial Intelligence, 134(1–2), 57–83.
→ For IBM Deep Blue vs. Garry Kasparov (1997).
Amazon. (2014). Introducing Amazon Alexa. Amazon Press Release.
→ For the rise of virtual assistants (Siri, Alexa).
Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence. (2025). AI Index Report 2025. Stanford University.
→ For AI trends, adoption rates, and investments (2023–2025).
Morgan Stanley. (2025). 5 AI Trends Shaping Innovation and ROI in 2025. Morgan Stanley Research.
→ For future trends like agentic AI, multimodal systems.
AWS. (2023). What’s the Difference Between Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning? Amazon Web Services.
→ For the difference between AI and ML.
GeeksforGeeks. (2023). Difference Between Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.
→ Another simple AI vs ML reference.
NVIDIA. (2025). Annual Financial Report 2020–2025. NVIDIA Investor Relations.
→ For the growth of Nvidia and GPUs fueling AI boom.
OpenAI. (2023). About OpenAI. Retrieved from https://openai.com
→ For OpenAI’s role and ChatGPT.
AI Magazine. (2024). Top 10 AI Leaders and Organizations. AI Magazine.
→ For key researchers and organizations like McCarthy, Turing, Hinton, Ng, Fei-Fei Li.
How do you see AI impacting your industry or daily life? What opportunities or concerns resonate most with you? Share your thoughts and let’s continue this crucial conversation.